Researcher Profiles

Giulia Biancon, Ph.D.
2023 Funding recipient
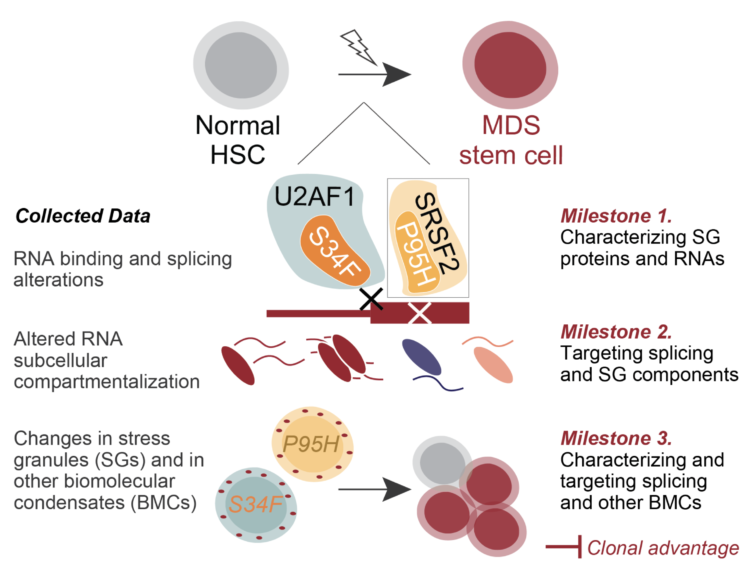
Mutant splicing factors induce aberrant RNA subcellular compartmentalization in MDS
EvansMDS Young Investigator Award
PROJECT SUMMARY
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are a group of blood diseases in which the bone marrow, a spongy tissue located in the center of most bones, is unable to produce enough healthy blood cells. Patients with MDS have therefore reduced white blood cells with high risk of infections, reduced red blood cells experiencing tiredness, and reduced platelets with excessive bleeding. The cause of this low production of healthy blood cells is the uncontrolled proliferation of altered blood cells within the bone marrow. These malignant cells, in up to 85% of MDS patients, present alterations in RNA splicing, a fundamental step in the processing of RNA molecules to produce diverse proteins and therefore cells with diverse functions.
My research focuses on understanding how altered RNA splicing factors promote the transformation of healthy blood cells into blood cells with cancer-like properties, leading to the development of MDS. My studies have recently shown that mutant splicing factors are directly linked to increased formation of stress granules, condensates of proteins and RNAs improving cellular adaptation to stress conditions, e.g. when cancer cells hyper-proliferate and the tissue in which they are located runs out of nutrients. The proposed project aims at further understanding the effect of altered RNA splicing factors on the aberrant compartmentalization of RNA molecules into stress granules and other biomolecular condensates, providing the basis for the development of novel effective treatments in MDS. I will first apply cutting-edge technologies to identify the stress granule components that drive enhanced stress granule formation and enhanced stress response in splicing factor-mutant cells (AIM 1). Then, I will evaluate if blocking RNA splicing process and/or stress response can specifically tackle down splicing factor-mutant blood cells without affecting healthy blood cells (AIM 2). Finally, I plan to investigate and modulate the effect of splicing factor mutations on other biomolecular condensates (AIM 3) to provide a more comprehensive picture of the link between altered RNA splicing and altered RNA subcellular compartmentalization in MDS.